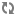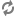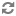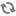In this screen you can choose between several security tools. Click on a link below to learn more.
Seguretat
“MSEC: Sistema de seguretat i auditoria” = Configure system security, permissions and audit
“Configuració avançada de les interfícies de xarxa i del tallafoc”

msecgui[43] is a graphic user interface for msec that allows to configure your system security according to two approaches:
It sets the system behaviour, msec imposes modifications to the system to make it more secure.
It carries on periodic checks automatically on the system in order to warn you if something seems dangerous.
msec uses the concept of "security levels" which are intended to configure a set of system permissions, which can be audited for changes or enforcement. Several of them are proposed by Mageia, but you can define your own customised security levels.
See the screenshot above
The first tab takes up the list of the different security tools with a button on the right side to configure them:
Firewall, also found in the MCC / Security / Set up your personal firewall
Updates, also found in MCC / Software Management / Update your system
msec itself with some information:
enabled or not
the configured Base security level
the date of the last Periodic checks and a button to see a detailed report and another button to execute the checks just now.
A click on the second tab or on the Security button leads to the same screen shown below.

Security levels:
After having checked the box Enable MSEC tool, this tab allows you by a double click to choose the security level that appears then in bold. If the box is not checked, the level « none » is applied. The following levels are available:
Level none. This level is intended if you do not want to use msec to control system security, and prefer tuning it on your own. It disables all security checks and puts no restrictions or constraints on system configuration and settings. Please use this level only if you are knowing what you are doing, as it would leave your system vulnerable to attack.
Level standard. This is the default configuration when installed and is intended for casual users. It constrains several system settings and executes daily security checks which detect changes in system files, system accounts, and vulnerable directory permissions. (This level is similar to levels 2 and 3 from past msec versions).
Level secure. This level is intended when you want to ensure your system is secure, yet usable. It further restricts system permissions and executes more periodic checks. Moreover, access to the system is more restricted. (This level is similar to levels 4 (High) and 5 (Paranoid) from old msec versions).
Besides those levels, different task-oriented security are also provided, such as the fileserver , webserver and netbook levels. Such levels attempt to pre-configure system security according to the most common use cases.
The last two levels called audit_daily and audit_weekly are not really security levels but rather tools for periodic checks only.
These levels are saved in
/etc/security/msec/level.<levelname>. You can define
your own customised security levels, saving them into specific files called
level.<levelname>, placed into the folder
/etc/security/msec/. This function is intended for
power users which require a customised or more secure system configuration.
Atenció
Keep in mind that user-modified parameters take precedence over default level settings.
Security alerts:
If you check the box , the security alerts generated by msec are going to be sent by local e-mail to the security administrator named in the nearby field. You can fill either a local user or a complete e-mail address (the local e-mail and the e-mail manager must be set accordingly). At last, you can receive the security alerts directly on your desktop. Check the relevant box to enable it.
Important
It is strongly advisable to enable the security alerts option in order to
immediately inform the security administrator of possible security
problems. If not, the administrator will have to regularly check the logs
files available in /var/log/security.
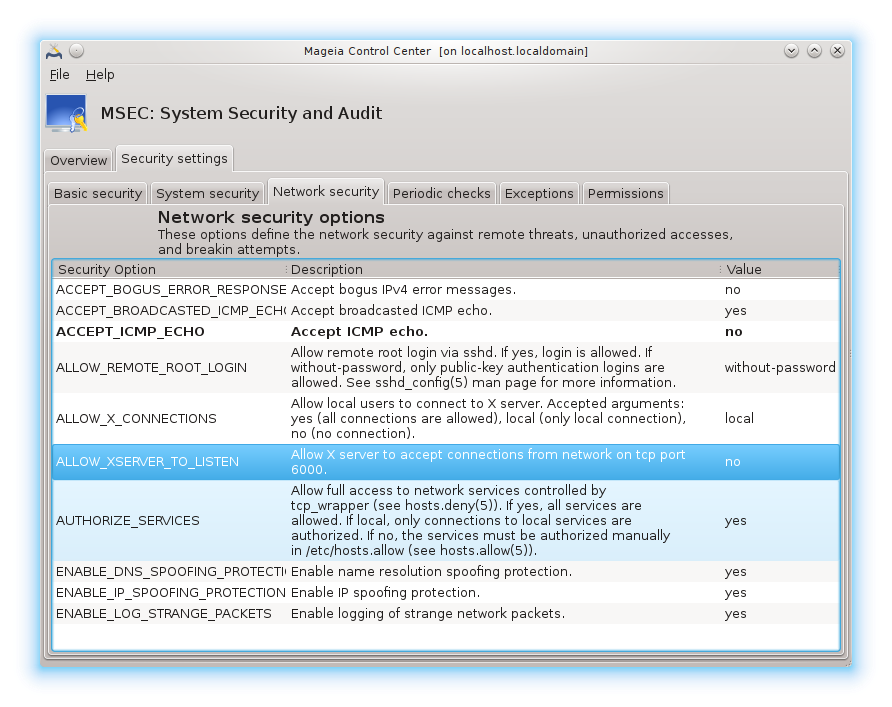
Security options:
Creating a customised level is not the only way to customise the computer
security, it is also possible to use the tabs presented here after to change
any option you want. Current configuration for msec is stored in
/etc/security/msec/security.conf. This file contains
the current security level name and the list of all the modifications done
to the options.
This tab displays all the security options on the left side column, a description in the centre column, and their current values on the right side column.

To modify an option, double click on it and a new window appears (see screenshot below). It displays the option name, a short description, the actual and default values, and a drop down list where the new value can be selected. Click on the button to validate the choice.

Atenció
Do not forget when leaving msecgui to save definitively your configuration using the menu . If you have changed the settings, msecgui allows you to preview the changes before saving them.

Periodic checks aim to inform the security administrator by means of security alerts of all situations msec thinks potentially dangerous.
This tab displays all the periodic checks done by msec and their frequency if the box is checked. Changes are done like in the previous tabs.

Sometimes alert messages are due to well known and wanted situations. In these cases they are useless and wasted time for the administrator. This tab allows you to create as many exceptions as you want to avoid unwanted alert messages. It is obviously empty at the first msec start. The screenshot below shows four exceptions.

To create an exception, click on the button

Select the wanted periodic check in the drop down list called Check and then, enter the Exception in the text area. Adding an exception is obviously not definitive, you can either delete it using the button of the Exceptions tab or modify it with a double clicK.
This tab is intended for file and directory permissions checking and enforcement.
Like for the security, msec owns different permissions levels (standard,
secure, ..), they are enabled accordingly with the chosen security
level. You can create your own customised permissions levels, saving them
into specific files called perm.<levelname> placed
into the folder /etc/security/msec/ . This function is
intended for power users which require a customised configuration. It is
also possible to use the tab presented here after to change any permission
you want. Current configuration is stored in
/etc/security/msec/perms.conf. This file contains the
list of all the modifications done to the permissions.

Default permissions are visible as a list of rules (a rule per line). You can see on the left side, the file or folder concerned by the rule, then the owner, then the group and then the permissions given by the rule. If, for a given rule:
the box Enforce is not checked, msec only checks if the defined permissions for this rule are respected and sends an alert message if not, but does not change anything.
the box Enforce is checked, then msec will rule the permissions respect at the first periodic check and overwrite the permissions.
Important
For this to work, the option CHECK_PERMS in the Periodic check tab must be configured accordingly.
To create a new rule, click on the button and fill the fields as shown in the example below. The joker * is allowed in the File field. “current” means no modification.

Click on the button to validate the choice and do not forget when leaving to save definitively your configuration using the menu . If you have changed the settings, msecgui allows you to preview the changes before saving them.
Nota
It is also possible to create or modify the rules by editing the
configuration file /etc/security/msec/perms.conf.
Atenció
Changes in the Permission tab (or directly in the configuration file) are taken into account at the first periodic check (see the option CHECK_PERMS in the Periodic checks tab). If you want them to be taken immediately into account, use the msecperms command in a console with root rights. You can use before, the msecperms -p command to know the permissions that will be changed by msecperms.
Atenció
Do not forget that if you modify the permissions in a console or in a file manager, for a file where the box Enforce is checked in the Permissions tab , msecgui will write the old permissions back after a while, accordingly to the configuration of the options CHECK_PERMS and CHECK_PERMS_ENFORCE in the Periodic Checks tab .

This tool[44] is found under the Security tab in the Mageia Control Center labelled "Set up your personal firewall". It is the same tool in the first tab of "Configure system security, permissions and audit".
A basic firewall is installed by default with Mageia. All the incoming connections from the outside are blocked if they aren't authorised. In the first screen above, you can select the services for which outside connection attempts are accepted. For your security, uncheck the first box - Everything (no firewall) - unless you want to disable the firewall, and only check the needed services.
It is possible to manually enter the port numbers to open. Click on and a new window is opened. In the field Other ports, enter the needed ports following these examples :
80/tcp : open the port 80 tcp protocol
24000:24010/udp : open all the ports from 24000 to 24010 udp protocol
The listed ports should be separated by a space.
If the box Log firewall messages in system logs is checked, the firewall messages will be saved in system logs

Nota
If you don't host specific services (web or mail server, file sharing, ...) it is completely possible to have nothing checked at all, it is even recommended, it won't prevent you from connecting to the internet.
The next screen deals with the Interactive Firewall options. These feature allow you to be warned of connection attempts if at least the first box Use Interactive Firewall is checked. Check the second box to be warned if the ports are scanned (in order to find a failure somewhere and enter your machine). Each box from the third one onwards corresponds to a port you opened in the two first screens; in the screenshot below, there are two such boxes: SSH server and 80:150/tcp. Check them to be warned each time a connection is attempted on those ports.
These warning are given by alert popups through the network applet.


In the last screen, choose which network interfaces are connected to the Internet and must be protected. Once the OK button is clicked, the necessary packages are downloaded.
Suggeriment
If you don't know what to choose, have a look in MCC tab Network & Internet, icon Set up a new network interface.

This tool[45]is present in the Mageia Control Center under the tab Security
It allows to give the regular users the needed rights to accomplish tasks usually done by the administrator.
Click on the little arrow before the item you want to drop down:

Most of the tools available in the Mageia Control Center are displayed in the left side of the window (see the screenshot above) and for each tool, a drop down list on the right side gives the choice between:
Default: The launch mode depends on the chosen security level. See in the same MCC tab, the tool "Configure system security, permissions and audit".
User password: The user password is asked before the tool launching.
Administrator password: The root password is asked before the tool launching
No password: The tool is launched without asking any password.

This page hasn't been written yet for lack of resources. If you think you can write this help, please contact the Doc team. Thanking you in advance.
You can start this tool from the command line, by typing drakinvictus as root.

This tool[46] is found in the Mageia Control Center, under the Security tab, labelled Parental Control. If you don't see this label, you have to install the drakguard package (not installed by default).
Drakguard is an easy way to set up parental controls on your computer to restrict who can do what, and at which times of day. Drakguard has three useful capabilities:
It restricts web access to named users to set times of day. It does this by controlling the shorewall firewall built into Mageia.
It blocks execution of particular commands by named users so these users can only execute what you accept them to execute.
It restricts access to websites, both manually defined through blacklists/whitelists, but also dynamically based on the content of the website. To achieve this Drakguard uses the leading opensource parental control blocker DansGuardian.
Avís
If your computer contains hard drive partitions that are formatted in Ext2, Ext3, or ReiserFS format you will see a pop up offering to configure ACL on your partitions. ACL stands for Access Control Lists, and is a Linux kernel feature that allows access to individual files to be restricted to named users. ACL is built into Ext4 and Btrfs file systems, but must be enabled by an option in Ext2, Ext3, or Reiserfs partitions. If you select 'Yes' to this prompt drakguard will configure all your partitions to support ACL, and will then suggest you reboot.
: If checked, the parental control is enabled and the access to Block programs tab is opened.
: If checked, all the websites are blocked, except the ones in the whitelist tab. Otherwise, all the websites are allowed, except the ones in the blacklist tab.
: Users on the left hand side will have their access restricted according to the rules you define. Users on the right hand side have unrestricted access so adult users of the computer are not inconvenienced. Select a user in the left hand side and click on to add him/her as an allowed user. Select an user in the right hand side and click on to remove him/her from the allowed users.
If checked, internet access is allowed with restrictions between the Start time and End time. It is totally blocked outside these time window.
[43] You can start this tool from the command line, by typing msecgui as root.
[44] You can start this tool from the command line, by typing drakfirewall as root.
[45] You can start this tool from the command line, by typing draksec as root.
[46] You can start this tool from the command line, by typing drakguard as root.